294/1 Asia Building (11th Floor), Phyathai, Bangkok
HPV vaccine
Most cervical cancers are associated with human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted infection. Widespread immunization with the HPV vaccine could reduce the impact of cervical cancer worldwide. Here’s what you need to know about the HPV vaccine.
What does the HPV vaccine do?
Various strains of HPV spread through sexual contact and are associated with most cases of cervical cancer. Gardasil 4 is an HPV vaccine approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and can be used for both girls and boys. This vaccine can prevent most cases of cervical cancer if given before a girl or woman is exposed to the virus. In addition, this vaccine can prevent vaginal and vulvar cancer in women, and can prevent genital warts and anal cancer in women and men. In theory, vaccinating boys against the types of HPV associated with cervical cancer might also help protect girls from the virus by possibly decreasing transmission. Certain types of HPV have also been linked to cancers in the mouth and throat, so the HPV vaccine likely offers some protection against these cancers, too.
Who is the HPV vaccine for and when should it be given?
The HPV vaccine is routinely recommended for girls and boys ages 11 or 12, although it can be given as early as age 9. It’s ideal for girls and boys to receive the vaccine before they have sexual contact and are exposed to HPV. Research has shown that receiving the vaccine at a young age isn’t linked to an earlier start of sexual activity. Once someone is infected with HPV, the vaccine might not be as effective or might not work at all. Also, response to the vaccine is better at younger ages than it is at older ages.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) now recommends that all 11- and 12-year-olds receive two doses of HPV vaccine at least six months apart, instead of the previously recommended three-dose schedule. Younger adolescents ages 9 and 10 and teens ages 13 and 14 also are able to receive vaccination on the updated two-dose schedule. Research has shown that the two-dose schedule is effective for children under 15. Teens and young adults who begin the vaccine series later, at ages 15 through 26, should continue to receive three doses of the vaccine.
Does the HPV vaccine offer benefits if you’re already sexually active?
Yes. Even if you already have one strain of HPV, you could still benefit from the vaccine because it can protect you from other strains that you don’t yet have. However, none of the vaccines can treat an existing HPV infection. The vaccines protect you only from specific strains of HPV you haven’t been exposed to already.
Does the HPV vaccine carry any health risks or side effects?
Overall, the effects are usually mild. The most common side effects of HPV vaccines include soreness, swelling or redness at the injection site. Sometimes dizziness or fainting occurs after the injection. Remaining seated for 15 minutes after the injection can reduce the risk of fainting. In addition, headaches, nausea, vomiting, fatigue or weakness also may occur.
Do women who’ve received the HPV vaccine still need to have Pap tests?
Yes. The HPV vaccine isn’t intended to replace Pap tests. Routine screening for cervical cancer through regular Pap tests beginning at age 21 remains an essential part of a woman’s preventive health care.
What can you do to protect yourself from cervical cancer if you’re not in the recommended vaccine age group?
HPV spreads through sexual contact — oral, vaginal or anal. To protect yourself from HPV, use a condom every time you have sex. In addition, don’t smoke. Smoking raises the risk of cervical cancer. To detect cervical cancer in the earliest stages, see your health care provider for regular Pap tests beginning at age 21. Seek prompt medical attention if you notice any signs or symptoms of cervical cancer — vaginal bleeding after sex, between periods or after menopause, pelvic pain, or pain during sex.
Reference : https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hpv-infection/in-depth/hpv-vaccine/art-20047292
Make Appointment





Relate content :

Your Guide to Sexual Health Clinics: Everything You Need to Know
Are you seeking information about sexual health clinics? Whether you're looking for routine check-ups, specific treatments, or simply want to learn more about your sexual health, this blog post is here to guide you. We'll discuss what sexual health clinics are, how to choose the right one, and provide a spotlight on sexual health clinics…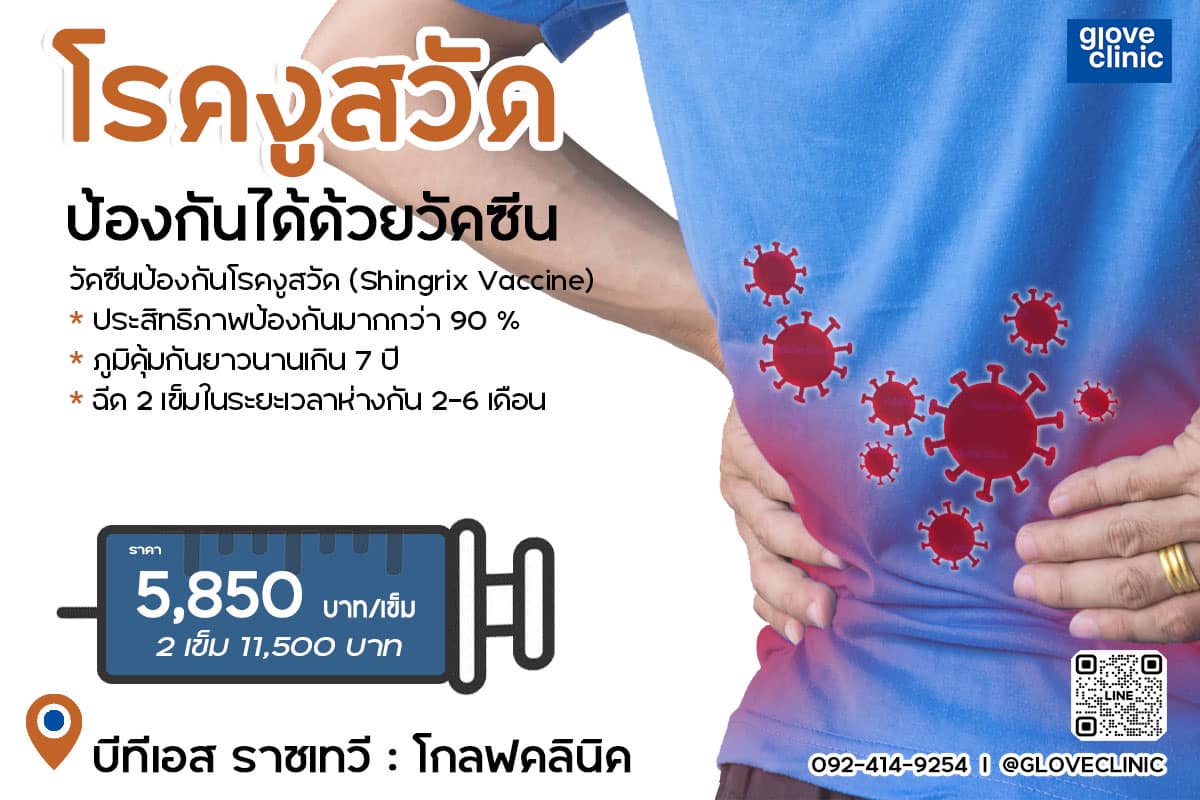
ฉีดวัคซีนงูสวัดที่ glove clinic
งูสวัดคือไวรัสชนิดหนึ่ง (Herpes zoster) ซึ่งเป็นเชื้อไวรัสตัวเดียวกันกับอีสุกอีใส (Varicella zoster) เมื่อเราติดเชื้อไวรัสอีสุกใสในวัยเด็กแล้ว ไวรัสสามารถที่จะหลบซ่อนได้ในร่างกายเป็นเวลานานหลายปี จนกระทั่งเมื่อร่างกายอ่อนแอ ไวรัสนั้นจึงออกมาทำให้เกิดอาการตุ่มน้ำใส ปวดแสบร้อนตามบริเวณที่เส้นประสาทต่าง ๆ ของร่างกายซึ่งเรียกกันว่างูสวัด
ตรวจ HIV รีวิวความรู้สำหรับการตรวจเอชไอวี (HIV test)
เอชไอวีคือไวรัสที่สามารถติดต่อได้จากการมีเพศสัมพันธ์, การใช้เข็มฉีดยาร่วมกัน, และการติดจากแม่สู่ลูก เมื่อติดเชื้อไวรัส HIV ไวรัสจะทำให้ภูมิคุ้มกันของร่างกายอ่อนแอลง และติดเชื้อโรคอื่น ๆ ได้ง่าย
ปีนี้มีคนไข้ป่วยด้วยไข้เลือดออกมากกว่า 2-3 ปีที่ผ่านมา
เนื่องจากว่าผู้คนกลับมาใช้ชีวิตปกติ มีการเดินทาง จึงพบการระบาดมากขึ้น โดยจากสถิติของกรมควบคุมโรคพบว่ามีผู้ป่วยด้วยไข้เลือดออกในประเทศไทยเกินกว่า 60,000 รายไปแล้วทั้งปี 2566 ไข้เลือดออกเป็นโรคที่ก่อให้เกิดความรุนแรงได้ทั้งในเด็กและผู้ใหญ่ โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งในคนที่เป็นซ้ำครั้งที่ 2 จะมีโอกาสเกิดภาวะช๊อคและเสียชีวิตได้มากขึ้น (โอกาสเสียชีวิตอยู่ราว ๆ 1:1,000) วัคซีนไข้เลือดออกรุ่นใหม่สามารถครอบคลุมได้ทั้ง 4 สายพันธุ์และทั้งนี้ผลการศึกษาพบว่าช่วยป้องกันการติดเชื้อได้ถึง 80% และลดโอกาสการนอนโรงพยาบาลได้ถึง 90% นอกจากนี้ยังสามารถฉีดได้ทั้งในคนที่เคยและไม่เคยเป็นไข้เลือดออกมาก่อน (วัคซีนไข้เลือดออกรุ่นเก่าไม่ควรฉีดในคนที่ยังไม่เคยเป็นไข้เลือดออก) สอบถามข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเรื่องวัคซีนไข้เลือดออกได้ที่ 092-414-9254, Line Official @gloveclinic (มีแอดข้างหน้า)
HIV แต่กำเนิด
ประเด็นร้อนที่ได้รับการพูดถึงอย่างมากในโลกออนไลน์ที่มีข้อความของนักศึกษาหญิงเปิดเผยว่าตัวเธอเองได้มีเพศสัมพันธ์แบบ one night stand เวลาไปเที่ยวกลางคืนบ่อยครั้ง และได้บอกความจริงว่าเธอเองมีเชื้อ HIV