294/1 Asia Building (11th Floor), Phyathai, Bangkok
ตรวจ HIV รีวิวความรู้สำหรับการตรวจเอชไอวี (HIV test)

In general, the symptoms of HIV infection depend on the stage of infection for each person. There are basically 3 stages including acute HIV infection, asymptomatic HIV infection (Asymptomatic HIV Infection) and the stage of immunodeficiency or like to be called AIDS (AIDS or Advanced Immunodeficiency Syndrome), respectively.
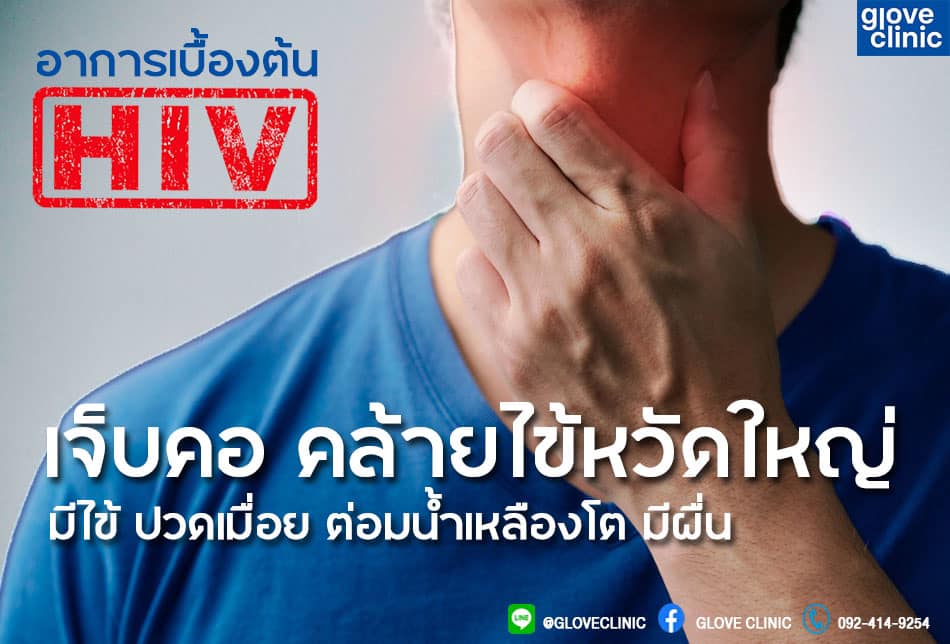
Symptoms in acute HIV infection may be seen in minority of patients who have just been infected with the virus for 10-14 days. The patient may have flu-like symptoms, namely high fever, sore throat, body aches. Some may have diarrhea or skin rashes. The physical examination will reveal enlarged lymph nodes. Patients with HIV infection in this stage may be misdiagnosed with influenza or dengue fever. Patients who are at risk of HIV infection should inform their sexual risks to healthcare providers in order to help improve the diagnosis.
Asymptomatic stage, which most people living with HIV are in this stage, is the stage where immune system is relatively intact. Therefore, it is less common for these patients to present with symptoms of opportunistic infection. After being infected with HIV in the early stage, patients will still be able to maintain in this asymptomatic stage for a few years without any signs or symptoms. Most CD4 values are normally more than 300-400 or even higher.
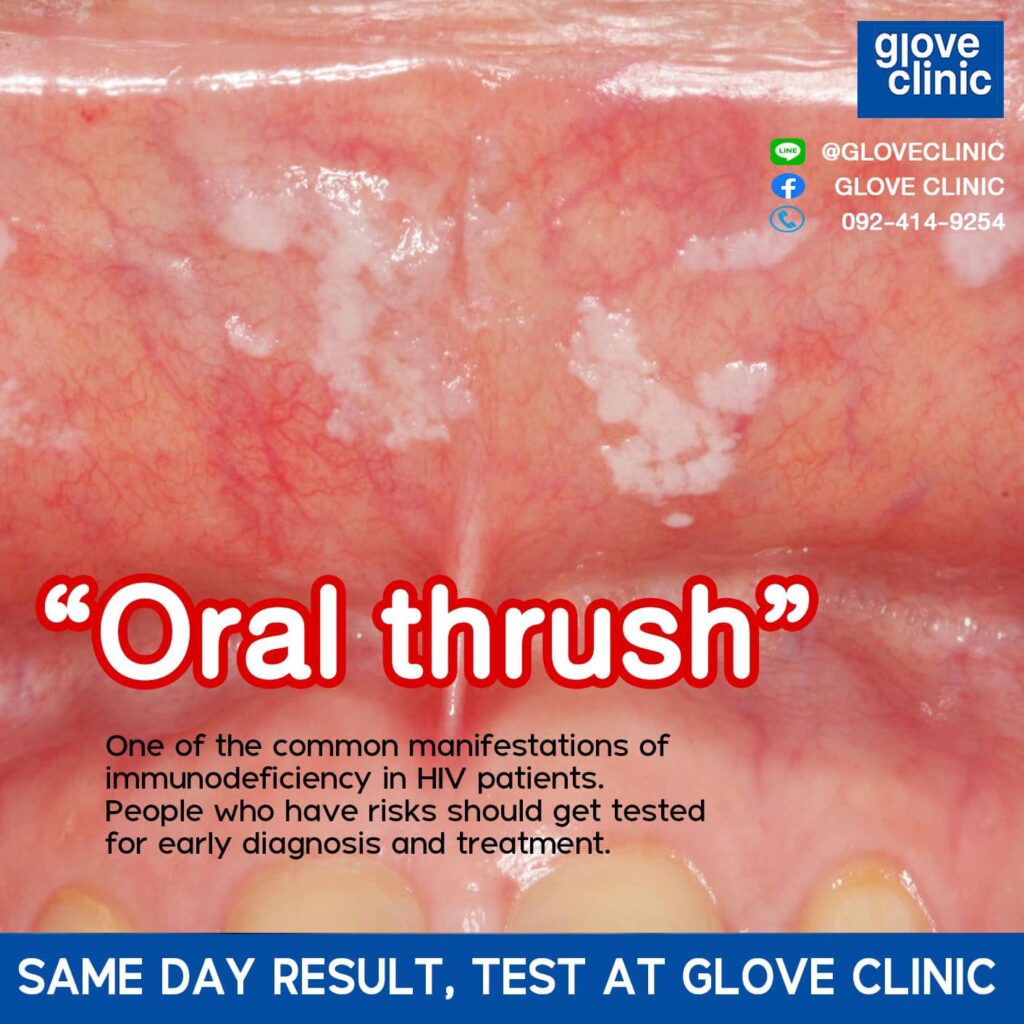
Immunodeficiency stage or AIDS if not diagnosed and not started on antiretroviral treatment (ART), patients infected with HIV will start to develop symptoms of immunodeficiency. Most likely, this will occur within 3-5 years after living with the virus. At the beginning, there could be intermittent diarrhea, chronic cough, and allergic rashes resembling rashes from insect bites. And when the immune deficiency is more profound (CD4 less than 200), patients may be at risk of having opportunistic infections, for example; tuberculosis (chronic cough, intermittent fevers, weight loss), pneumocystis pneumonia (dry cough, difficulty breathing), oral candidiasis (oral thrush). Patients in this stage need to receive antiretroviral and also antibiotic (if needed), to correct their immune system and to treat opportunistic infections. Once treated properly, patients can resume their normal lives and daily activities like before having the illness.
HIV treatment is best if antiretroviral treatment has been started when the patient has no symptoms of complications. Therefore, everyone who is at risk of HIV infection should have an HIV screening test. Early HIV detection can help reduce the chance of immunodeficiency stage in people living with HIV.
Make Appointment





Relate content :
ฉีดวัคซีนงูสวัดที่ glove clinic
งูสวัดคือไวรัสชนิดหนึ่ง (Herpes zoster) ซึ่งเป็นเชื้อไวรัสตัวเดียวกันกับอีสุกอีใส (Varicella zoster) เมื่อเราติดเชื้อไวรัสอีสุกใสในวัยเด็กแล้ว ไวรัสสามารถที่จะหลบซ่อนได้ในร่างกายเป็นเวลานานหลายปี จนกระทั่งเมื่อร่างกายอ่อนแอ ไวรัสนั้นจึงออกมาทำให้เกิดอาการตุ่มน้ำใส ปวดแสบร้อนตามบริเวณที่เส้นประสาทต่าง ๆ ของร่างกายซึ่งเรียกกันว่างูสวัด
ตรวจ HIV รีวิวความรู้สำหรับการตรวจเอชไอวี (HIV test)
เอชไอวีคือไวรัสที่สามารถติดต่อได้จากการมีเพศสัมพันธ์, การใช้เข็มฉีดยาร่วมกัน, และการติดจากแม่สู่ลูก เมื่อติดเชื้อไวรัส HIV ไวรัสจะทำให้ภูมิคุ้มกันของร่างกายอ่อนแอลง และติดเชื้อโรคอื่น ๆ ได้ง่าย
ปีนี้มีคนไข้ป่วยด้วยไข้เลือดออกมากกว่า 2-3 ปีที่ผ่านมา
เนื่องจากว่าผู้คนกลับมาใช้ชีวิตปกติ มีการเดินทาง จึงพบการระบาดมากขึ้น โดยจากสถิติของกรมควบคุมโรคพบว่ามีผู้ป่วยด้วยไข้เลือดออกในประเทศไทยเกินกว่า 60,000 รายไปแล้วทั้งปี 2566 ไข้เลือดออกเป็นโรคที่ก่อให้เกิดความรุนแรงได้ทั้งในเด็กและผู้ใหญ่ โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งในคนที่เป็นซ้ำครั้งที่ 2 จะมีโอกาสเกิดภาวะช๊อคและเสียชีวิตได้มากขึ้น (โอกาสเสียชีวิตอยู่ราว ๆ 1:1,000) วัคซีนไข้เลือดออกรุ่นใหม่สามารถครอบคลุมได้ทั้ง 4 สายพันธุ์และทั้งนี้ผลการศึกษาพบว่าช่วยป้องกันการติดเชื้อได้ถึง 80% และลดโอกาสการนอนโรงพยาบาลได้ถึง 90% นอกจากนี้ยังสามารถฉีดได้ทั้งในคนที่เคยและไม่เคยเป็นไข้เลือดออกมาก่อน (วัคซีนไข้เลือดออกรุ่นเก่าไม่ควรฉีดในคนที่ยังไม่เคยเป็นไข้เลือดออก) สอบถามข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเรื่องวัคซีนไข้เลือดออกได้ที่ 092-414-9254, Line Official @gloveclinic (มีแอดข้างหน้า)
HIV แต่กำเนิด
ประเด็นร้อนที่ได้รับการพูดถึงอย่างมากในโลกออนไลน์ที่มีข้อความของนักศึกษาหญิงเปิดเผยว่าตัวเธอเองได้มีเพศสัมพันธ์แบบ one night stand เวลาไปเที่ยวกลางคืนบ่อยครั้ง และได้บอกความจริงว่าเธอเองมีเชื้อ HIV
อาการของเอดส์เป็นอย่างไร ทำความรู้จักกับเอดส์
เอดส์ คืออะไร แท้จริงแล้วเอดส์ไม่ใช่โรค หากแต่คือระยะสุดท้ายของการติดเชื้อ HIV ซึ่ง HIV นั่นเองคือไวรัสที่ทำลายภูมิคุ้มกันของร่างกาย โดยเซลล์หลักที่ถูกเล่นงานโดยไวรัสก็คือเม็ดเลือดขาว CD4 ซึ่งเป็นเซลล์ที่บัญชาการระบบภูมิคุ้มกันของร่างกาย ซึ่งเอดส์ในภาษาอังกฤษก็คือ AIDS ย่อมาจาก Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome กำเนิดของการเรียกชื่อว่าเอดส์ เดือนมิถุนายน ค.ศ. 1981 ในวารสารของกรมควบคุมโรค ประเทศสหรัฐอเมริกาได้รายงานว่ามีเกย์หนุ่ม 5 คนมีอาการปอดอักเสบจากเชื้อรา และได้รับการรักษาในโรงพยาบาลที่ Los Angeles โดย 2 รายเสียชีวิต และนอกจากนี้ทั้ง 5 คนยังพบการติดเชื้อไวรัส CMV และมีเชื้อราในช่องปากร่วมด้วย ซึ่งเชื้อต่าง ๆ ที่เล่ามานั้นมักเจอในผู้ป่วยที่มีภูมิคุ้มกันบกพร่อง ในขณะนั้นโลกยังไม่ได้รู้จักกับไวรัส HIV ว่าเป็นสาเหตุตั้งต้นของสิ่งที่เกิดขึ้น การเรียกภาวะนี้ในยุคแรกจึงได้เรียกว่า AIDS หรือ “เอดส์” ซึ่งย่อมาจาก acquired immunodeficiency syndrome อาการของเอดส์แตกต่างกับ HIV ยังไง เอดส์คือชื่อระยะที่ 3…